Subdivide
Default Shortcut: C
Menu Path: Subdivision > Subdivide
Description
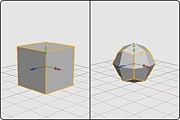
The Subdivide command will subdivide all active objects one level. When an object is subdivided it has two elements: an editable control mesh and an underlying refined mesh. The refined mesh (also sometimes called the "iso surface") represents the visible object, but it can't be edited directly (use the Refine Control Mesh command if you want to edit this mesh). Instead it is edited by making changes to the coarser polygon control mesh.
When an object is subdivided for the first time, its original geometry is used for the control mesh, and the refined mesh is a smoothed version of that geometry. An object can be subdivided multiple times, which results in a smoother refined mesh which is controlled by the same control mesh.
In Silo you can subdivide anything, whether it be an object with faces or a sequence of edges used as a line segment. Many actions, when performed with a subdivided shape, will use the subdivided mesh rather than the control mesh. These include Lathe Object, Extrusion Object, Path Extrusion, and Boolean operations. This allows you to create a profile for a lathe in rough form, then subdivide (or partial subdivide) the profile to a desired smoothness, adjusting the shape with the outer control mesh, then create the lathe with the inner subdivided object.
Sticky Functionality
Press and hold the keyboard shortcut for this command to temporarily preview the next subdivision level. Release the shortcut to go back to the current subdivision level.
Notes
- When you subdivide an object several times, each level of the subdivision is saved in memory, so subdividing a large object several times can use a lot of memory. When you Unsubdivide, the subdivided shapes are still retained in memory, allowing you to go back to the higher level of subdivision without the program having to recalculate the subdivided mesh.
- Subdivide can be performed on whole objects only.
- Subdivide will be applied to all active objects, no matter the selection mode.
- Subdividing an instance will cause its parent object to be subdivided.